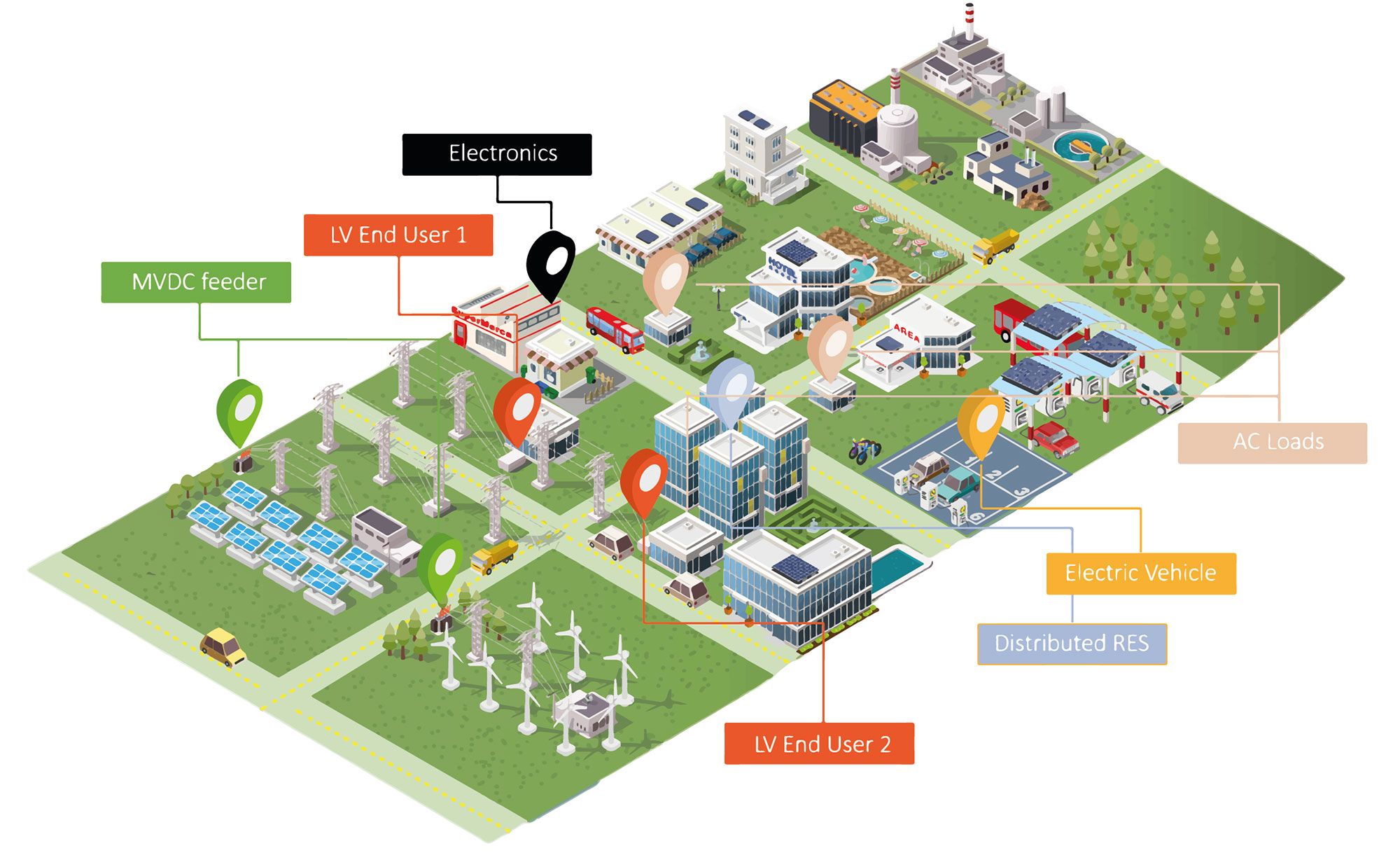
Clean local energy and modern electrical equipment run on direct current (DC)
Most electricity grid infrastructure remains centralised and uses alternating current (AC)
Conversion from DC to AC and back to DC leads to power losses, which add to the losses due to long distance electricity transmission.
- multiple conversion stages reduce efficiency and reliability of power systems
- the low technology readiness levels of DC technology means
- DC technologies lack standardisation
- AC-DC grid interconnection requires extra effort
- digital infrastructures may be vulnerable to cyberattacks